RESEARCH PROJECTS
Click a tab to view more about that research project.
Simultaneous magnetic resonance and optical elastography acquisitions
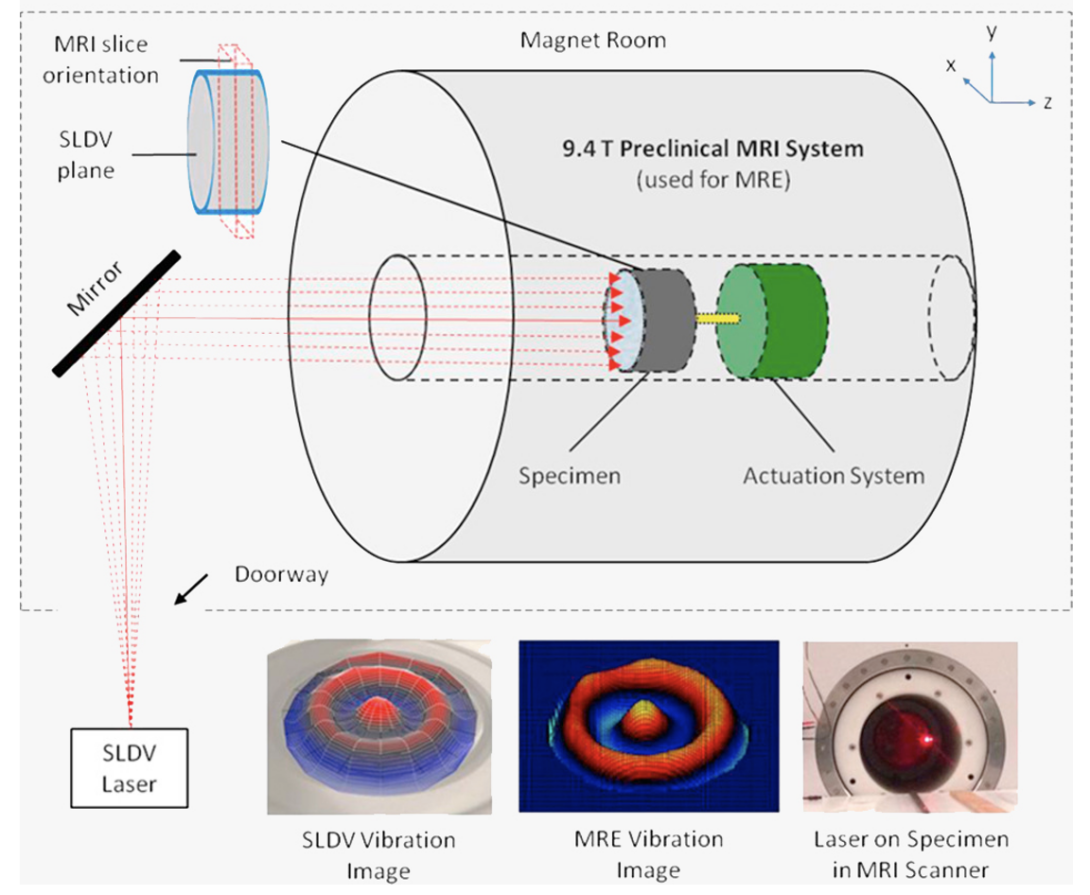
Magnetic Resonance Elastography (MRE) with 3D inversion and Optical Elastography (OE) with averaged 1D curve fitting were used to derive complex shear moduli from each imaging modality. [Link]
Demonstration of Concurrent Tensile Testing and Magnetic Resonance Elastography
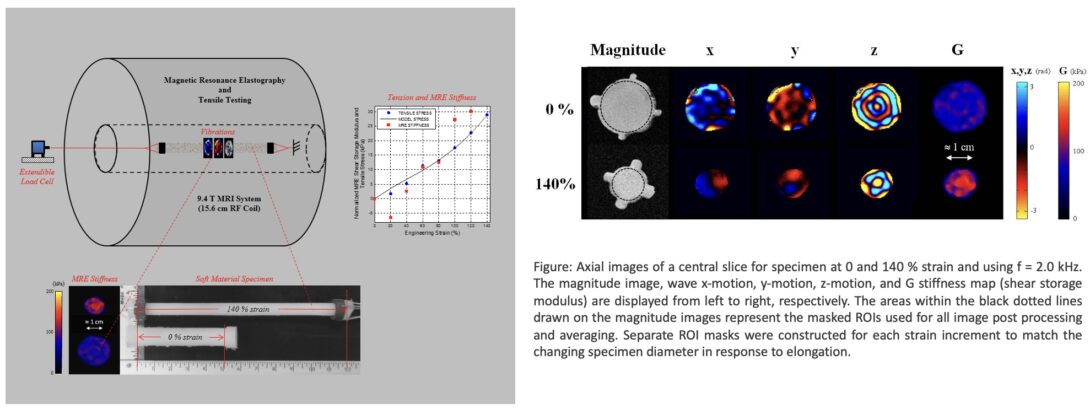
Development of a device for simultaneous tensile testing and MRE.[Link]
Sample interval modulation (SLIM) for simultaneous acquisition of displacement vector
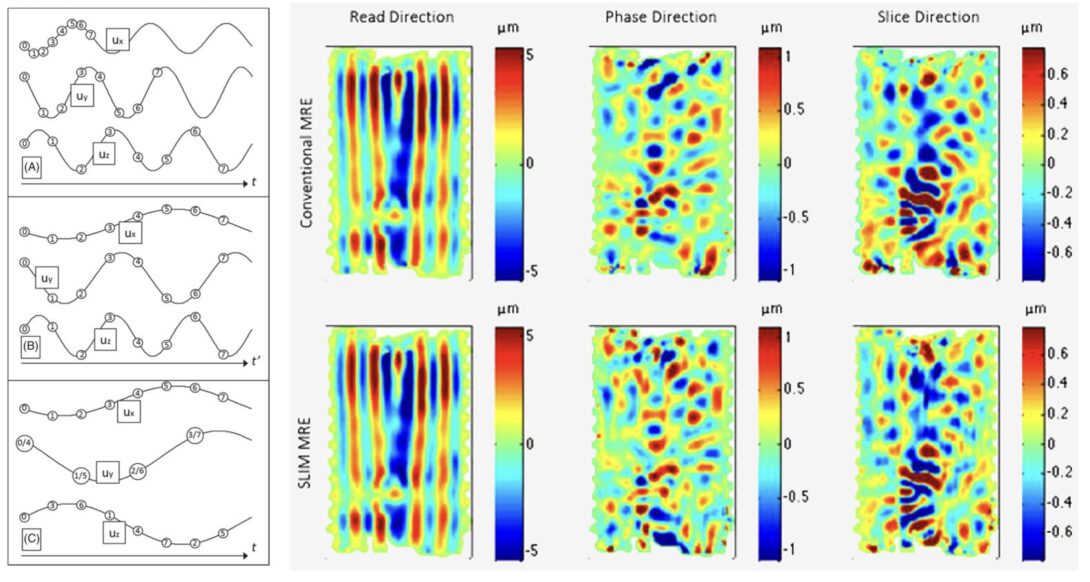
Sample interval modulation for the simultaneous acquisition of 3D displacement vector data in MRE.[Link]
Concurrent 3D acquisition of diffusion tensor imaging and magnetic resonance elastography displacement data (dMRE)
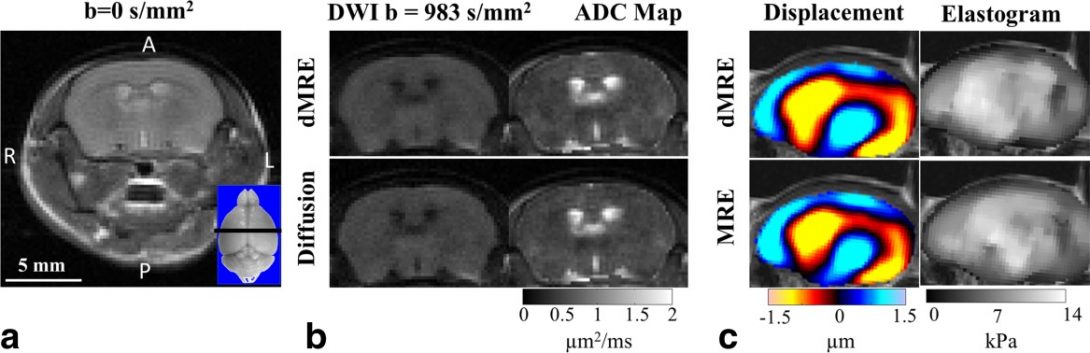
Comparison of in vivo dMRE results with conventional MRE and diffusion experiments. [Link]
Multi-frequency DTIMRE (mDTIMRE) for human brain
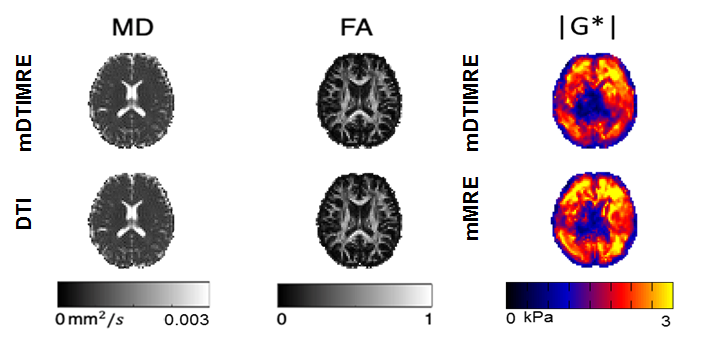
The mDTIMRE was achieved by ensuring the same diffusion encoding using experiment parameters with different mechanical frequencies, while fulfilling the timing condition of simultaneous acquisition. By applying a multifrequency dual elasto-visco inversion approach, the effective image resolution of mechanical property maps is improved and enables quantitatively assessment of tissue properties in brain sub-regions.
Prostate Cancer Diagnosis Using MRE
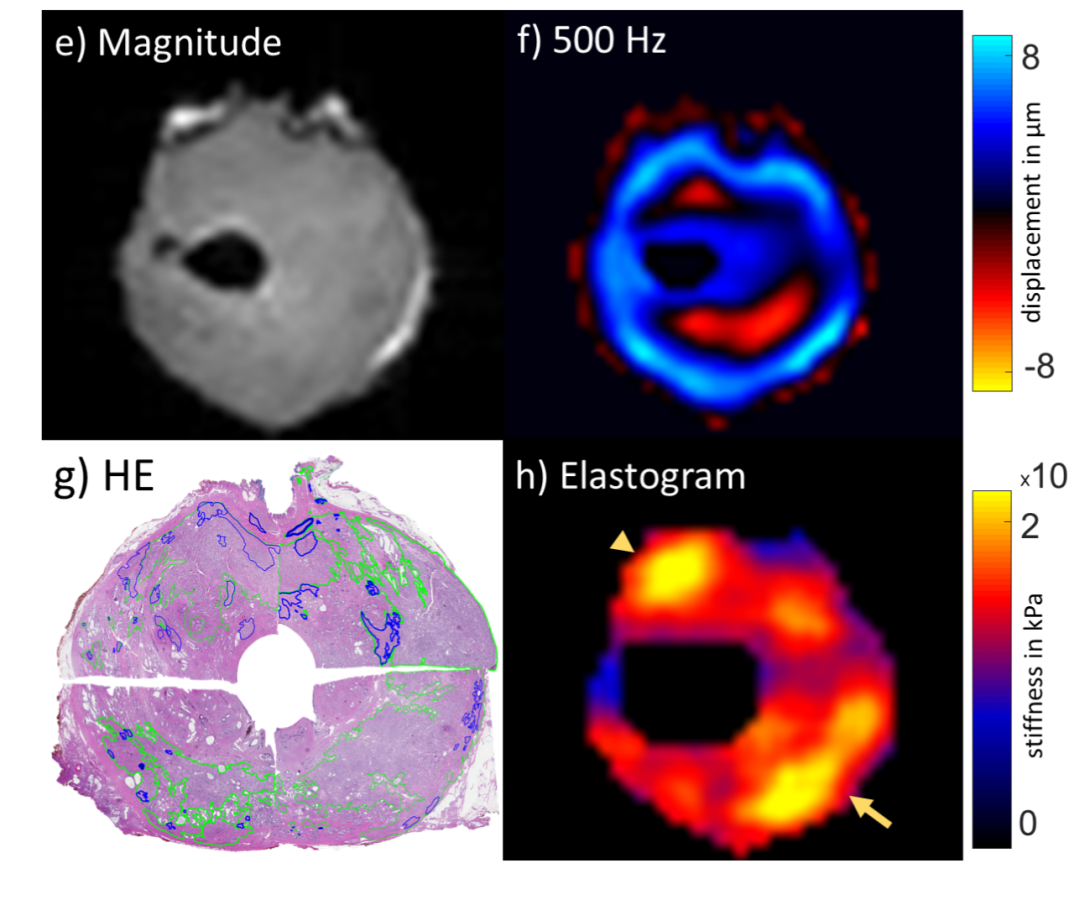
The purpose of this research is to detect and localize prostate cancer ex vivo using human prostate samples without pathology fixation or prior radiation therapy.
SLIM-MRE Study on a Mouse Model of Familial Alzheimer's Disease
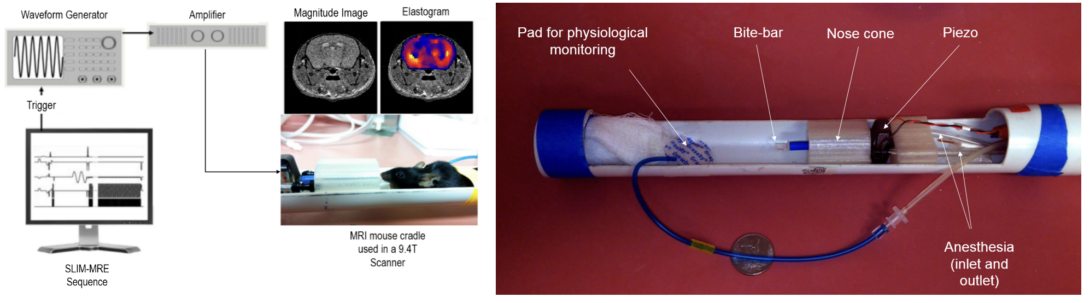
The goal of the research is to use SLIM-MRE, a fast motion encoding concept developed by our group [link], in order to examine the early diagnostic potential of MRE for Alzheimer’s disease (AD). If MRE was sensitive to early stages of AD, then the technique would qualify as a non-invasive monitor for novel, potential treatments for AD.
Examination of Lysed Tissue Samples Using Tabletop MRE
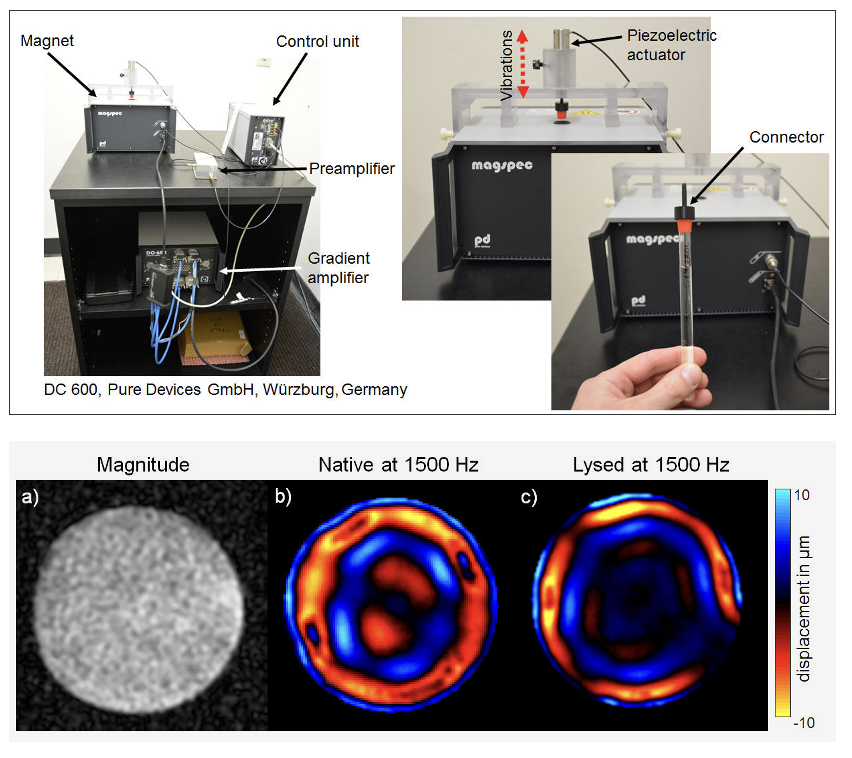
Figure: (Top)Porcine kidney specimen scanned in axial orientation in a glass capillary. (Bottom) (a) The magnitude image shows a homogeneous tissue distribution. Compared to (b) the native shear wave image, waves in (c) the lysed image show a shorter wave length, indicating a decrease in stiffness.